中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 133-142.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00091
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-04-14
修回日期:2023-10-24
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-03-19
通讯作者:
苏永中
作者简介:苏永中(E-mail: suyzh@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Fangjiao An1( ), Yongzhong Su2(
), Yongzhong Su2( ), Ziru Niu3, Tingna Liu2
), Ziru Niu3, Tingna Liu2
Received:2023-04-14
Revised:2023-10-24
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-19
Contact:
Yongzhong Su
摘要:
荒漠绿洲过渡带人工固沙梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)林生长发育过程中,土壤生物多样性的演变研究是认识干旱区植物-土壤相互作用的重要内容。在河西走廊中段临泽绿洲边缘选择不同栽植时间序列(0、3、6、11、19、28、46 a)的固沙梭梭林,取冠层下和冠层外的表层土样(0~10 cm),研究固沙梭梭林建立后土壤线虫群落组成和多样性变化,探究线虫群落对植被-土壤系统恢复的指示作用。结果表明:在研究区共发现15个属,Eucephalobus和Acrobeloides为优势属,食细菌线虫(BF)为优势营养类群,占线虫总数50.3%~94.1%。梭梭生长显著提高土壤线虫总数、食细菌线虫丰度和线虫多样性。线虫富集指数(EI)和结构指数(SI)均小于50,土壤食物网随梭梭种植年限增加先稳定后逐渐退化。冗余分析表明,土壤化学性质变化(电导率EC、C/N和土壤有机碳SOC)显著影响线虫群落分布,EC对线虫属总变异解释率最高(32.7%)。土壤线虫作为生物指标揭示了植被-土壤生态系统的演变过程。
中图分类号:
安芳娇, 苏永中, 牛子儒, 刘婷娜. 干旱区荒漠绿洲过渡带建植梭梭( Haloxylon ammodendron )林后土壤线虫群落演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 133-142.
Fangjiao An, Yongzhong Su, Ziru Niu, Tingna Liu. Evolution of soil nematode community after establishment of Haloxylon ammodendron plantations in an arid desert-oasis ecotone[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 133-142.
| 种植 年限/a | pH | 电导率EC/(μS·cm-1) | 全碳TC/(g·kg-1) | 全氮TN/(g·kg-1) | 全磷TP/(g·kg-1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |||||
| 0 | 9.28±0.16Ac | 9.28±0.16Aa | 130.27±3.93Ae | 130.27±3.93Ac | 4.98±0.11Ad | 4.98±0.11Ac | 0.28±0.04Ac | 0.28±0.04Ac | 0.46±0.02Ad | 0.46±0.02Ac | ||||
| 3 | 10.05±0.13Aab | 9.41±0.08Ba | 306.00±10.39Ade | 130.00±5.20Bc | 5.32±0.03Ad | 5.13±0.20Abc | 0.22±0.00Ad | 0.19±0.01Ad | 0.49±0.01Acd | 0.47±0.01Ac | ||||
| 6 | 10.08±0.02Aab | 9.59±0.25Ba | 438.00±91.39Acd | 202.27±68.49Bbc | 6.96±0.53Ac | 6.28±0.19Ab | 0.30±0.01Ac | 0.21±0.02Ad | 0.56±0.02Acd | 0.53±0.04Abc | ||||
| 11 | 10.03±0.05Aab | 9.61±0.21Ba | 522.00±100.64Ac | 231.00±51.10Bab | 7.40±0.16Abc | 6.32±0.50Ab | 0.38±0.03Ab | 0.28±0.02Ac | 0.57±0.00Ac | 0.54±0.03Abc | ||||
| 19 | 10.09±0.01Aa | 9.57±0.37Ba | 713.67±96.26Abc | 253.10±15.53Bab | 8.43±0.88Aab | 7.63±0.92Aa | 0.38±0.01Ab | 0.33±0.00Abc | 0.68±0.07Aab | 0.65±0.08Aa | ||||
| 28 | 9.87±0.20Ab | 9.59±0.23Ba | 721.00±71.34Ab | 287.63±104.60Bab | 8.72±1.65Aa | 7.87±1.34Aa | 0.52±0.01Aa | 0.39±0.07Aa | 0.67±0.08Aabc | 0.64±0.08Aa | ||||
| 46 | 9.98±0.12Aab | 9.47±0.15Ba | 987.00±227.66Aa | 321.67±45.01Ba | 9.64±0.23Aa | 8.29±0.78Aa | 0.52±0.03Aa | 0.38±0.02Aab | 0.70±0.10Aa | 0.63±0.06Aab | ||||
| 年限 | *** | ns | *** | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | ||||
| 位置 | *** | *** | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||
| 年限×位置 | *** | *** | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||
| 种植年限/a | 土壤有机碳SOC/(g·kg-1) | 碳氮比C/N | 速效氮AN/(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷AP/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾AK/(mg·kg-1) | |||||||||
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |||||
| 0 | 0.35±0.03Ad | 0.35±0.03Ad | 1.29±0.11Ad | 1.29±0.11Ac | 25.38±2.13Ab | 25.38±2.13Abc | 2.33±0.29Ac | 2.33±0.29Ad | 103.33±5.77Ad | 103.33±5.77Ad | ||||
| 3 | 0.42±0.04Ad | 0.30±0.02Bd | 1.95±0.19Ad | 1.57±0.04Ac | 20.96±0.52Bcd | 21.93±0.16Ac | 2.52±0.50Ac | 2.79±0.18Ad | 120.00±0.00Ad | 96.67±5.77Bd | ||||
| 6 | 1.22±0.09Ac | 0.71±0.13Bcd | 4.02±0.41Ac | 3.39±0.87Ab | 19.63±0.65Bd | 22.81±1.62Ac | 3.40±0.81Ac | 3.56±0.89Acd | 210.00±65.57Ac | 130.00±17.32Bd | ||||
| 11 | 1.63±0.13Ab | 1.14±0.19Bbc | 4.38±0.66Abc | 4.06±0.78Ab | 19.86±1.15Bd | 29.56±1.56Aab | 13.37±0.46Ab | 5.84±2.12Bbc | 353.33±41.63Ab | 156.67±15.28Bcd | ||||
| 19 | 1.89±0.07Ab | 1.31±0.22Bb | 4.91±0.14Aab | 4.04±0.62Ab | 23.04±0.91Bbcd | 30.26±1.21Aab | 13.94±4.70Ab | 6.45±1.52Bb | 380.00±0.00Ab | 200.00±20.00Bc | ||||
| 28 | 2.80±0.54Aa | 1.85±0.62Ba | 5.33±0.92Aa | 4.63±0.72Aab | 24.33±0.73Bbc | 30.84±1.26Aab | 26.85±3.47Aa | 11.92±2.40Ba | 510.00±60.83Aa | 300.00±26.46Bb | ||||
| 46 | 2.76±0.13Aa | 2.03±0.20Ba | 5.28±0.43Aa | 5.37±0.82Aa | 29.39±1.09Ba | 33.76±1.52Aa | 23.45±3.29Aa | 11.11±2.09Ba | 546.67±25.17Aa | 453.33±94.52Ba | ||||
| 年限 | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||
| 位置 | *** | ns | ** | *** | *** | |||||||||
| 年限×位置 | *** | ns | ns | * | ns | |||||||||
表1 不同固沙年限土壤化学性质
Table 1 Soil chemical properties in different sand-fixation years
| 种植 年限/a | pH | 电导率EC/(μS·cm-1) | 全碳TC/(g·kg-1) | 全氮TN/(g·kg-1) | 全磷TP/(g·kg-1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |||||
| 0 | 9.28±0.16Ac | 9.28±0.16Aa | 130.27±3.93Ae | 130.27±3.93Ac | 4.98±0.11Ad | 4.98±0.11Ac | 0.28±0.04Ac | 0.28±0.04Ac | 0.46±0.02Ad | 0.46±0.02Ac | ||||
| 3 | 10.05±0.13Aab | 9.41±0.08Ba | 306.00±10.39Ade | 130.00±5.20Bc | 5.32±0.03Ad | 5.13±0.20Abc | 0.22±0.00Ad | 0.19±0.01Ad | 0.49±0.01Acd | 0.47±0.01Ac | ||||
| 6 | 10.08±0.02Aab | 9.59±0.25Ba | 438.00±91.39Acd | 202.27±68.49Bbc | 6.96±0.53Ac | 6.28±0.19Ab | 0.30±0.01Ac | 0.21±0.02Ad | 0.56±0.02Acd | 0.53±0.04Abc | ||||
| 11 | 10.03±0.05Aab | 9.61±0.21Ba | 522.00±100.64Ac | 231.00±51.10Bab | 7.40±0.16Abc | 6.32±0.50Ab | 0.38±0.03Ab | 0.28±0.02Ac | 0.57±0.00Ac | 0.54±0.03Abc | ||||
| 19 | 10.09±0.01Aa | 9.57±0.37Ba | 713.67±96.26Abc | 253.10±15.53Bab | 8.43±0.88Aab | 7.63±0.92Aa | 0.38±0.01Ab | 0.33±0.00Abc | 0.68±0.07Aab | 0.65±0.08Aa | ||||
| 28 | 9.87±0.20Ab | 9.59±0.23Ba | 721.00±71.34Ab | 287.63±104.60Bab | 8.72±1.65Aa | 7.87±1.34Aa | 0.52±0.01Aa | 0.39±0.07Aa | 0.67±0.08Aabc | 0.64±0.08Aa | ||||
| 46 | 9.98±0.12Aab | 9.47±0.15Ba | 987.00±227.66Aa | 321.67±45.01Ba | 9.64±0.23Aa | 8.29±0.78Aa | 0.52±0.03Aa | 0.38±0.02Aab | 0.70±0.10Aa | 0.63±0.06Aab | ||||
| 年限 | *** | ns | *** | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | ||||
| 位置 | *** | *** | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||
| 年限×位置 | *** | *** | ns | ns | ns | |||||||||
| 种植年限/a | 土壤有机碳SOC/(g·kg-1) | 碳氮比C/N | 速效氮AN/(mg·kg-1) | 速效磷AP/(mg·kg-1) | 速效钾AK/(mg·kg-1) | |||||||||
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |||||
| 0 | 0.35±0.03Ad | 0.35±0.03Ad | 1.29±0.11Ad | 1.29±0.11Ac | 25.38±2.13Ab | 25.38±2.13Abc | 2.33±0.29Ac | 2.33±0.29Ad | 103.33±5.77Ad | 103.33±5.77Ad | ||||
| 3 | 0.42±0.04Ad | 0.30±0.02Bd | 1.95±0.19Ad | 1.57±0.04Ac | 20.96±0.52Bcd | 21.93±0.16Ac | 2.52±0.50Ac | 2.79±0.18Ad | 120.00±0.00Ad | 96.67±5.77Bd | ||||
| 6 | 1.22±0.09Ac | 0.71±0.13Bcd | 4.02±0.41Ac | 3.39±0.87Ab | 19.63±0.65Bd | 22.81±1.62Ac | 3.40±0.81Ac | 3.56±0.89Acd | 210.00±65.57Ac | 130.00±17.32Bd | ||||
| 11 | 1.63±0.13Ab | 1.14±0.19Bbc | 4.38±0.66Abc | 4.06±0.78Ab | 19.86±1.15Bd | 29.56±1.56Aab | 13.37±0.46Ab | 5.84±2.12Bbc | 353.33±41.63Ab | 156.67±15.28Bcd | ||||
| 19 | 1.89±0.07Ab | 1.31±0.22Bb | 4.91±0.14Aab | 4.04±0.62Ab | 23.04±0.91Bbcd | 30.26±1.21Aab | 13.94±4.70Ab | 6.45±1.52Bb | 380.00±0.00Ab | 200.00±20.00Bc | ||||
| 28 | 2.80±0.54Aa | 1.85±0.62Ba | 5.33±0.92Aa | 4.63±0.72Aab | 24.33±0.73Bbc | 30.84±1.26Aab | 26.85±3.47Aa | 11.92±2.40Ba | 510.00±60.83Aa | 300.00±26.46Bb | ||||
| 46 | 2.76±0.13Aa | 2.03±0.20Ba | 5.28±0.43Aa | 5.37±0.82Aa | 29.39±1.09Ba | 33.76±1.52Aa | 23.45±3.29Aa | 11.11±2.09Ba | 546.67±25.17Aa | 453.33±94.52Ba | ||||
| 年限 | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | ||||
| 位置 | *** | ns | ** | *** | *** | |||||||||
| 年限×位置 | *** | ns | ns | * | ns | |||||||||
| 固沙 年限/a | 线虫总数 | 食细菌线虫BF | 食真菌线虫FF | 植物寄生线虫PP | 捕食/杂食线虫OP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |
| 0 | 5.33±1.31Ad | 5.33±1.31Ab | 4.00±0.00Ad | 4.00±0.00Ab | 1.33±0.31Ab | 1.33±0.31Aab | 0.00±0.00Aa | 0.00±0.00Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab |
| 3 | 44.33±10.18Acd | 11.67±3.15Bab | 36.33±11.16Acd | 8.33±3.15Bab | 6.67±0.58Aab | 1.00±0.73Bb | 0.00±0.00Aa | 2.33±0.08Aa | 1.33±0.31Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab |
| 6 | 99.33±22.72Abc | 61.33±11.67Ba | 85.67±24.53Abc | 47.00±9.04Bab | 8.67±1.57Aab | 8.33±1.79Ba | 0.00±0.00Aa | 1.00±0.73Aab | 5.00±1.73Ab | 5.00±1.73Aab |
| 11 | 143.33±45.52Aab | 62.00±12.05Ba | 116.00±23.81Ab | 52.33±13.14Ba | 6.33±0.69Aab | 7.33±1.51Bab | 0.00±0.00Aa | 0.00±0.00Ab | 20.00±6.00Aa | 2.33±1.04Ab |
| 19 | 148.67±43.94Aab | 61.67±12.53Ba | 123.00±28.58Ab | 49.00±12.26Bab | 8.67±1.77Aab | 1.33±0.31Bab | 1.67±0.89Aa | 1.00±0.73Aab | 15.33±5.15Aa | 10.33±2.45Aa |
| 28 | 136.33±40.34Ab | 60.00±11.68Ba | 129.00±43.38Ab | 54.33±18.46Ba | 6.00±1.29Aab | 3.33±0.77Bab | 1.33±0.31Aa | 0.00±0.00Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab | 2.33±1.04Ab |
| 46 | 228.00±61.46Aa | 41.00±16.64Bab | 213.33±54.80Aa | 38.67±10.34Bab | 13.67±2.51Aa | 2.33±0.08Bab | 0.00±0.00Aa | 0.00±0.00Ab | 1.00±0.73Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab |
| 年限 | ** | * | ** | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | * |
| 位置 | *** | *** | * | ns | ns | |||||
| 年限× 位置 | * | ** | ns | ns | ns | |||||
表2 不同固沙年限土壤线虫总数及营养类群
Table 2 Total numbers of soil nematodes and nematode trophic groups in different sand-fixation years
| 固沙 年限/a | 线虫总数 | 食细菌线虫BF | 食真菌线虫FF | 植物寄生线虫PP | 捕食/杂食线虫OP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |
| 0 | 5.33±1.31Ad | 5.33±1.31Ab | 4.00±0.00Ad | 4.00±0.00Ab | 1.33±0.31Ab | 1.33±0.31Aab | 0.00±0.00Aa | 0.00±0.00Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab |
| 3 | 44.33±10.18Acd | 11.67±3.15Bab | 36.33±11.16Acd | 8.33±3.15Bab | 6.67±0.58Aab | 1.00±0.73Bb | 0.00±0.00Aa | 2.33±0.08Aa | 1.33±0.31Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab |
| 6 | 99.33±22.72Abc | 61.33±11.67Ba | 85.67±24.53Abc | 47.00±9.04Bab | 8.67±1.57Aab | 8.33±1.79Ba | 0.00±0.00Aa | 1.00±0.73Aab | 5.00±1.73Ab | 5.00±1.73Aab |
| 11 | 143.33±45.52Aab | 62.00±12.05Ba | 116.00±23.81Ab | 52.33±13.14Ba | 6.33±0.69Aab | 7.33±1.51Bab | 0.00±0.00Aa | 0.00±0.00Ab | 20.00±6.00Aa | 2.33±1.04Ab |
| 19 | 148.67±43.94Aab | 61.67±12.53Ba | 123.00±28.58Ab | 49.00±12.26Bab | 8.67±1.77Aab | 1.33±0.31Bab | 1.67±0.89Aa | 1.00±0.73Aab | 15.33±5.15Aa | 10.33±2.45Aa |
| 28 | 136.33±40.34Ab | 60.00±11.68Ba | 129.00±43.38Ab | 54.33±18.46Ba | 6.00±1.29Aab | 3.33±0.77Bab | 1.33±0.31Aa | 0.00±0.00Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab | 2.33±1.04Ab |
| 46 | 228.00±61.46Aa | 41.00±16.64Bab | 213.33±54.80Aa | 38.67±10.34Bab | 13.67±2.51Aa | 2.33±0.08Bab | 0.00±0.00Aa | 0.00±0.00Ab | 1.00±0.73Ab | 0.00±0.00Ab |
| 年限 | ** | * | ** | * | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | * |
| 位置 | *** | *** | * | ns | ns | |||||
| 年限× 位置 | * | ** | ns | ns | ns | |||||
| 线虫属 | 营养类型 | c-p值 | 线虫属的优势度 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 a | 3 a | 6 a | 11 a | 19 a | 28 a | 46 a | ||||||||||
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层 下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |||
| Mesorhabditis | BF | 1 | — | — | ++ | — | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | — | ++ | ++ | — |
| Eucephalobus | BF | 2 | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Acrobeles | BF | 2 | — | — | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Acrobeloides | BF | 2 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Eumonhystera | BF | 2 | — | — | — | — | — | ++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Ceratoplectus | BF | 2 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ++ | — |
| Paraphelenchus | FF | 2 | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | — | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Aphelenchoides | FF | 2 | — | — | — | — | ++ | — | — | — | ++ | — | — | — | — | — |
| Tylolaimophorus | FF | 3 | — | — | ++ | — | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | — | + | ++ |
| Filenchus | PP | 2 | — | — | — | +++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Psilenchus | PP | 2 | — | — | — | +++ | — | ++ | — | — | ++ | — | + | — | — | — |
| Rotylenchus | PP | 3 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ++ | ++ | — | — | — | — |
| Prodorylaimium | OP | 5 | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | — | ++ | ++ | — | — | — | — |
| Aporcelaimium | OP | 5 | — | — | ++ | — | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | — | ++ | + | — |
| Discolaimus | OP | 5 | — | — | — | — | ++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
表3 不同固沙年限土壤线虫属的营养类型、c-p值和优势度
Table 3 Nutrient types, c-p values and dominance of nematodes in different sand-fixation years
| 线虫属 | 营养类型 | c-p值 | 线虫属的优势度 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 a | 3 a | 6 a | 11 a | 19 a | 28 a | 46 a | ||||||||||
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层 下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |||
| Mesorhabditis | BF | 1 | — | — | ++ | — | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | — | ++ | ++ | — |
| Eucephalobus | BF | 2 | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Acrobeles | BF | 2 | — | — | ++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Acrobeloides | BF | 2 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Eumonhystera | BF | 2 | — | — | — | — | — | ++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Ceratoplectus | BF | 2 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ++ | — |
| Paraphelenchus | FF | 2 | +++ | +++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | — | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Aphelenchoides | FF | 2 | — | — | — | — | ++ | — | — | — | ++ | — | — | — | — | — |
| Tylolaimophorus | FF | 3 | — | — | ++ | — | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | — | + | ++ |
| Filenchus | PP | 2 | — | — | — | +++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Psilenchus | PP | 2 | — | — | — | +++ | — | ++ | — | — | ++ | — | + | — | — | — |
| Rotylenchus | PP | 3 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ++ | ++ | — | — | — | — |
| Prodorylaimium | OP | 5 | — | — | — | — | — | — | + | — | ++ | ++ | — | — | — | — |
| Aporcelaimium | OP | 5 | — | — | ++ | — | ++ | ++ | +++ | ++ | ++ | +++ | — | ++ | + | — |
| Discolaimus | OP | 5 | — | — | — | — | ++ | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 固沙 年限/a | 丰富度指数 | 香农-维纳多样性指数 | 均匀度指数 | 优势度指数 | 总成熟度指数 | 线虫通路指数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |
| 0 | 0.40±0.06e | 0.40±0.06c | 0.23±0.40Ab | 0.23±0.40Ac | 0.33±0.07Ab | 0.33±0.07Ab | 0.83±0.29Aa | 0.83±0.29Aa | 2.00±0.00Aa | 2.00±0.00Ab | 0.83±0.29Aa | 0.83±0.29Aa |
| 3 | 1.33±0.18bc | 1.19±0.32ab | 1.11±0.33Aa | 0.75±0.10Ab | 0.84±0.10Ba | 0.93±0.12Aa | 0.40±0.11Ab | 0.50±0.00Ab | 2.13±0.13Aa | 2.00±0.00Ab | 0.82±0.07Aa | 0.67±0.58Aa |
| 6 | 2.04±0.19a | 1.65±0.42a | 1.38±0.16Aa | 1.59±0.08Aa | 0.76±0.01Ba | 0.88±0.08Aa | 0.33±0.04Ab | 0.40±0.07Abc | 2.15±0.09Aa | 2.39±0.24Aa | 0.89±0.10Aa | 0.74±0.30Aa |
| 11 | 1.38±0.23bc | 1.30±0.36ab | 1.17±0.18Aa | 0.96±0.38Ab | 0.70±0.08Bab | 0.81±0.08Aa | 0.48±0.15Ab | 0.38±0.14Abc | 2.33±0.60Aa | 2.04±0.14Ab | 0.96±0.04Aa | 0.86±0.17Aa |
| 19 | 1.42±0.02b | 1.31±0.25ab | 1.30±0.09Aa | 1.22±0.34Aab | 0.72±0.03Bab | 0.77±0.05Aa | 0.32±0.06Ab | 0.24±0.02Ac | 2.42±0.09Aa | 2.45±0.13Aa | 0.94±0.05Aa | 0.98±0.03Aa |
| 28 | 0.96±0.26cd | 0.95±0.33abc | 1.12±0.11Aa | 0.95±0.39Ab | 0.77±0.09Ba | 0.78±0.15Aa | 0.40±0.07Ab | 0.48±0.18Abc | 2.01±0.02Aa | 2.06±0.10Ab | 0.94±0.06Aa | 0.92±0.14Aa |
| 46 | 0.87±0.10d | 0.86±0.24bc | 1.07±0.07Aa | 0.81±0.23Ab | 0.64±0.03Bab | 0.78±0.15Aa | 0.45±0.03Ab | 0.53±0.12Ab | 2.00±0.05Aa | 2.02±0.04Ab | 0.94±0.01Aa | 0.92±0.09Aa |
| 年限 | *** | ns | * | * | * | * | * | * | ns | ** | ns | ns |
| 位置 | ns | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | ||||||
| 年限× 位置 | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||||||
表4 不同固沙年限线虫生态指数
Table 4 Nematode ecological indices in in different sand-fixation years
| 固沙 年限/a | 丰富度指数 | 香农-维纳多样性指数 | 均匀度指数 | 优势度指数 | 总成熟度指数 | 线虫通路指数 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | 冠层下 | 冠层外 | |
| 0 | 0.40±0.06e | 0.40±0.06c | 0.23±0.40Ab | 0.23±0.40Ac | 0.33±0.07Ab | 0.33±0.07Ab | 0.83±0.29Aa | 0.83±0.29Aa | 2.00±0.00Aa | 2.00±0.00Ab | 0.83±0.29Aa | 0.83±0.29Aa |
| 3 | 1.33±0.18bc | 1.19±0.32ab | 1.11±0.33Aa | 0.75±0.10Ab | 0.84±0.10Ba | 0.93±0.12Aa | 0.40±0.11Ab | 0.50±0.00Ab | 2.13±0.13Aa | 2.00±0.00Ab | 0.82±0.07Aa | 0.67±0.58Aa |
| 6 | 2.04±0.19a | 1.65±0.42a | 1.38±0.16Aa | 1.59±0.08Aa | 0.76±0.01Ba | 0.88±0.08Aa | 0.33±0.04Ab | 0.40±0.07Abc | 2.15±0.09Aa | 2.39±0.24Aa | 0.89±0.10Aa | 0.74±0.30Aa |
| 11 | 1.38±0.23bc | 1.30±0.36ab | 1.17±0.18Aa | 0.96±0.38Ab | 0.70±0.08Bab | 0.81±0.08Aa | 0.48±0.15Ab | 0.38±0.14Abc | 2.33±0.60Aa | 2.04±0.14Ab | 0.96±0.04Aa | 0.86±0.17Aa |
| 19 | 1.42±0.02b | 1.31±0.25ab | 1.30±0.09Aa | 1.22±0.34Aab | 0.72±0.03Bab | 0.77±0.05Aa | 0.32±0.06Ab | 0.24±0.02Ac | 2.42±0.09Aa | 2.45±0.13Aa | 0.94±0.05Aa | 0.98±0.03Aa |
| 28 | 0.96±0.26cd | 0.95±0.33abc | 1.12±0.11Aa | 0.95±0.39Ab | 0.77±0.09Ba | 0.78±0.15Aa | 0.40±0.07Ab | 0.48±0.18Abc | 2.01±0.02Aa | 2.06±0.10Ab | 0.94±0.06Aa | 0.92±0.14Aa |
| 46 | 0.87±0.10d | 0.86±0.24bc | 1.07±0.07Aa | 0.81±0.23Ab | 0.64±0.03Bab | 0.78±0.15Aa | 0.45±0.03Ab | 0.53±0.12Ab | 2.00±0.05Aa | 2.02±0.04Ab | 0.94±0.01Aa | 0.92±0.09Aa |
| 年限 | *** | ns | * | * | * | * | * | * | ns | ** | ns | ns |
| 位置 | ns | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns | ||||||
| 年限× 位置 | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||||||
| RDA轴 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒙特卡罗排列检验 | R2=0.476 F=26.2 P=0.002*** | |||
| 特征值 | 0.4279 | 0.0327 | 0.0106 | 0.005 |
| 累积解释变异/% | 42.79 | 46.06 | 47.12 | 47.61 |
| 线虫属相关性 | 0.9333 | 0.4264 | 0.3507 | 0.3215 |
| 累计解释拟合变异/% | 89.3 | 96.12 | 98.33 | 99.36 |
表5 线虫属与环境因子的RDA排序综述
Table 5 RDA ordination summary for nematode genera and environmental factors
| RDA轴 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蒙特卡罗排列检验 | R2=0.476 F=26.2 P=0.002*** | |||
| 特征值 | 0.4279 | 0.0327 | 0.0106 | 0.005 |
| 累积解释变异/% | 42.79 | 46.06 | 47.12 | 47.61 |
| 线虫属相关性 | 0.9333 | 0.4264 | 0.3507 | 0.3215 |
| 累计解释拟合变异/% | 89.3 | 96.12 | 98.33 | 99.36 |
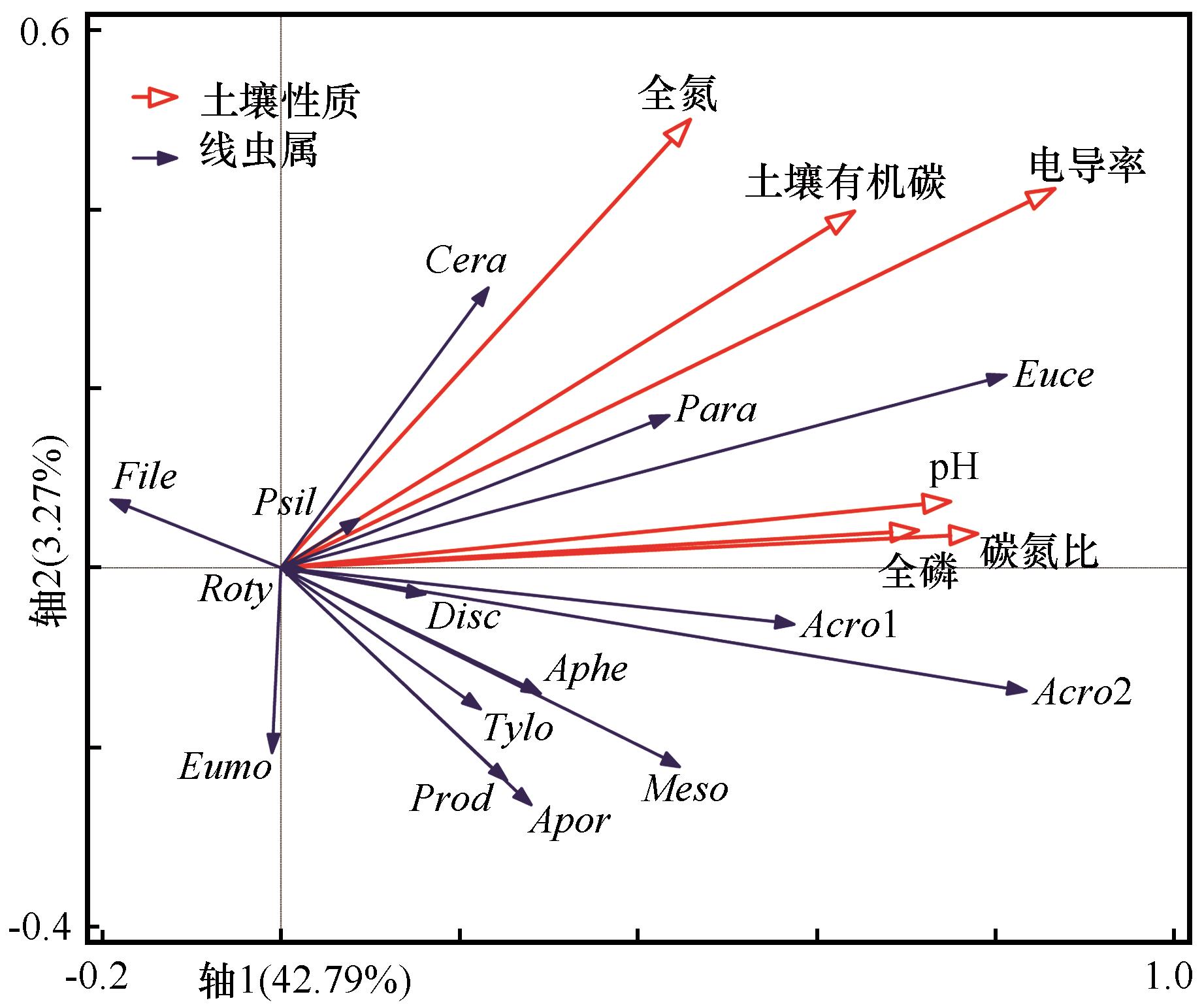
图3 土壤线虫属与环境因子的冗余分析注:Meso-Mesorhabditis, Euce-Eucephalobus, Acro1-Acrobeles, Acro2-Acrobeloides, Cera-Ceratoplectus, Para-Paraphelenchus, Aphe-Aphelenchoides, Tylo-Tylolaimophorus, Psil-Psilenchus, Roty-Rotylenchus, Prod-Prodorylaimium, Apor-Aporcelaimium, Disc-Discolaimus, Eumo-Eumonhystera, File-Filenchus
Fig.3 Redundancy analysis diagram of the relationships between soil nematode genera and environmental factors
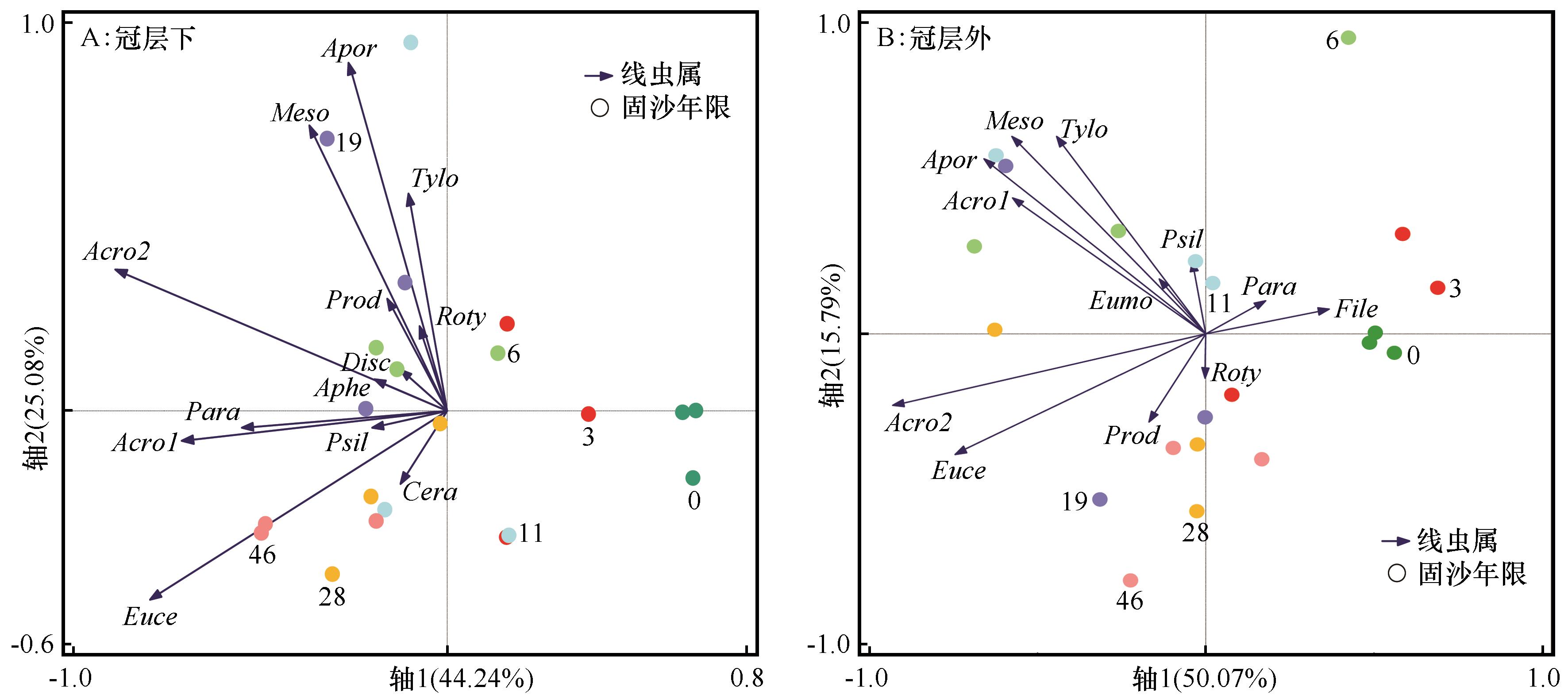
图5 不同固沙年限线虫属分布注:Meso-Mesorhabditis, Euce-Eucephalobus, Acro1-Acrobeles, Acro2-Acrobeloides, Cera-Ceratoplectus, Para-Paraphelenchus,Aphe-Aphelenchoides, Tylo-Tylolaimophorus, Psil-Psilenchus, Roty-Rotylenchus, Prod-Prodorylaimium,Apor-Aporcelaimium, Disc-Discolaimus, Eumo-Eumonhystera, File-Filenchus
Fig.5 Distribution of nematode genera in different sand-fixation years
| 1 | Neher D A.Ecology of plant and free-living nematodes in natural and agricultural soil[J].Annual Review of Phytopathology,2010,48:371-394. |
| 2 | Yeates G W.Nematodes as soil indicators: functional and biodiversity aspects[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2003,37:199-210. |
| 3 | Zhao J, Wang F M, Li J,et al.Effects of experimental nitrogen and/or phosphorus additions on soil nematode communities in a secondary tropical forest[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2014,75:1-10. |
| 4 | Alan K, Raquel C H, Sara Sánchez-Moreno,et al.The abundance,diversity,and metabolic footprint of soil nematodes is highest in high elevation alpine grasslands[J].Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution,2016,4:1-12. |
| 5 | Zhang X K, Liang W J, Jiang D M,et al.Soil nematode community structure in a Chinese sand dune system[J].Helminthologia,2007,44:204-209. |
| 6 | Klass J R, Peters D P C, Trohan J M,et al.Nematodes as an indicator of plant-soil interactions associated with desertification[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2012,58:66-77. |
| 7 | Zhi D J, Nan W B, Ding X X,et al.Soil nematode community succession in stabilized sand dunes in the Tengger Desert,China[J].Australian Journal of Soil Research,2009,47:508-517. |
| 8 | Guan P T, Zhang X K, Yu J,et al.Variation of soil nematode community composition with increasing sand-fixation year of Caragana microphylla:bioindication for desertification restoration[J].Ecological Engineering,2015,81:93-101. |
| 9 | Yudai Kitagami, Toko Tanikawa, Yosuke Matsuda.Effects of microhabitats and soil conditions on structuring patterns of nematode communities in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) plantation forests under temperate climate conditions[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2020,151(1). |
| 10 | Peter Salamún, Vladimíra Hanzelová, Dana Miklisová,et al.The effects of vegetation cover on soil nematode communities in various biotopes disturbed by industrial emissions[J].Science of the Total Environment,2017,592:106-114. |
| 11 | Su Y Z, Zhao W Z, Su P X,et al.Ecological effects of desertification control and desertified land reclamation in an oasis-desert ecotone in an arid region:a case study in Hexi Corridor, Northwest China[J].Ecological Engineering, 2007, 29: 117-124 . |
| 12 | Liu J L, Wang Y G, Yang X H,et al.Genetic variation in seed and seedling traits of six Haloxylon ammodendron shrub provenances in desert areas of China[J].Agroforestry Systems,2011,81:135-146. |
| 13 | Zhang K, Su Y Z, Liu T N,et al.Leaf C∶N∶P stoichiometrical and morphological traits of Haloxylon ammodendron over plantation age sequences in an oasis-desert ecotone in North China[J].Ecological Research,2016,31:449-457. |
| 14 | Zhang K, Su Y Z, Wang T,et al.Soil properties and herbaceous characteristics in an age sequence of Haloxylon ammodendron plantations in an oasis-desert ecotone of northwestern China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2016,8:960-972. |
| 15 | Yu K L, Wang G H.Long-term impacts of shrub plantations in a desert-oasis ecotone: accumulation of soil nutrients, salinity and development of herbaceour layer[J].Land Degradation and Development,2018,29:2681-2693. |
| 16 | Zhu Y J, Jia Z Q.Soil water utilization characteristics of Haloxylon ammodendron plantation with different age during summer[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2011,31(6):341-346. |
| 17 | 吉小敏,宁虎森,梁继业,等.不同水分条件下梭梭和多花柽柳苗期光合特性及抗旱性比较[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(2):399-406. |
| 18 | Cao Y F, Li Y, Li C H,et al.Relationship between presence of the desert shrub Haloxylon ammodendron and microbial communities in two soils with contrasting textures[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2016,103:93-100. |
| 19 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000. |
| 20 | Yeates G W, Bongers T, De Goede R G,et al.Feeding habits in soil nematode families and genera-an outline for soil ecologists[J].Journal of Nematology,1993,25:315-331. |
| 21 | Mulder C, Schouten A J, Hund-Rinke K,et al.The use of nematodes in ecological soil classification and assessment concepts[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2005,62:278-289. |
| 22 | Ferris H, Bongers T, de Goede R G M.A framework for soil food web diagnostics: extension of the nematode faunal analysis concept[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2001,18(1):13-29. |
| 23 | 苏永中,刘婷娜.流动沙地建植人工固沙梭梭林的土壤演变过程[J].土壤学报,2020,57(1):84-91. |
| 24 | Pen-Mouratov S, Rakhimbaev M, Steinberger Y.Seasonal and spatial variation in nematode communities in a Negev Desert Ecosystem[J].Journal of Nematology,2003,35:157-166. |
| 25 | Zhi D, Li H, Nan W.Nematode communities in the artificially vegetated belt with or without irrigation in the Tengger Desert, China[J].European Journal of Soil Biology,2008,44:238-246. |
| 26 | Wei C Z, Zheng H F, Li Q,et al.Nitrogen addition regulates soil nematode community composition through ammonium suppression[J].PLoS One,2012,7(8). |
| 27 | Yuan B, Li Z, Liu H,et al.Microbial biomass and activity in salt affected soils under and conditions[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2007,35:319-328. |
| 28 | Su Y Z, Wang X F, Yang R,et al.Soil fertility,salinity and nematode diversity influenced by Tamarix ramosissima in different habitats in an arid desert oasis[J].Environmental Management,2012,50:226-236. |
| 29 | Rousk J, Brookes P C, Bååth E.Contrasting soil pH effects on fungal and bacterial growth suggest functional redundancy in carbon mineralization[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2009,75(6):1589-1596. |
| 30 | 王雪峰,苏永中,杨荣.黑河中游绿洲不同开垦年限农田土壤线虫群落特征[J].应用生态学报,2010,21(8):2125-2131. |
| 31 | Viketoft M, Palmborg C, Sohlenius B,et al.Plant species effects on soil nematode communities in experimental grasslands[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2005,30:90-103. |
| 32 | 贾慧,王晟强,郑子成,等.植茶年限对土壤团聚体线虫群落结构的影响[J].生态学报,2020,40(6):2130-2140. |
| 33 | Bastow J L.Resource quality in a soil food web[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2012,48:501-510. |
| 34 | De Deyn G B, Raaijmakers C E, van Ruijven J,et al.Plant species identity and diversity effects on different trophic levels of nematodes in the soil food web[J].Oikos,2004,106:576-586. |
| 35 | 周立峰,杨荣,赵文智.荒漠人工固沙植被区土壤结皮斥水性发展特征[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(3):185-192. |
| [1] | 包天玲, 刘继亮, 苑峰, 李寅龙, 贾振宇, 潘成臣. 科尔沁沙质草地植物群落对增温的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 151-160. |
| [2] | 孙小霞, 冯怡琳, 王永珍, 罗维成, 杨竟艺, 史宏亮, 刘继亮. 祁连山东大河林区煤矿修复对地表甲虫多样性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 176-186. |
| [3] | 甘开元, 张金霞, 陈丽娟, 席海洋, 张斌武, 雍天, 卫雨西. 乌兰布和沙漠沿黄河段植物群落特征及空间分异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 180-190. |
| [4] | 陶海璇, 郭春秀, 马俊梅, 王忠文, 赵赫然, 宋达成, 何芳兰. 干旱沙区土壤结皮发育对草本植物土壤种子库的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 89-97. |
| [5] | 韩高玲, 霍建强, 赵燕翘, 虎瑞, 张志山, 黄日辉, 薛书文. 鄂尔多斯高原砒砂岩地区草本物种组成及多样性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 243-251. |
| [6] | 乔荣荣, 黄海涛, 董春媛, 罗立辉, 常学礼. 宁夏沿黄人工绿洲农田格局对景观多样性的影响——以卫宁平原灌区为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 21-27. |
| [7] | 潘颜霞, 回嵘, 李新荣. 中国沙漠微生物分布及特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 244-256. |
| [8] | 王生棠, 盖迎春, 王少昆, 张晓龙, 杨映. 黑河流域植物物种多样性对土地利用变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 221-232. |
| [9] | 李星, 马媛, 李星, 高君亮, 辛智鸣, 卢琦. 乌兰布和沙漠植物群落相异性及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 187-194. |
| [10] | 许文文, 赵燕翘, 王楠, 赵洋. 人工生物土壤结皮对草本植物群落组成与多样性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 204-211. |
| [11] | 宋兆斌, 辛智鸣, 朱雅娟. 内蒙古荒漠-草原过渡带灌木群落特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 104-112. |
| [12] | 赵啸龙, 谢玉鸿, 马旭君, 王少昆. 科尔沁沙质草地不同恢复年限草本层群落结构及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 134-141. |
| [13] | 詹瑾, 韩丹, 杨红玲, 李玉霖. 科尔沁沙地植被恢复过程中群落组成及多样性演变特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 194-206. |
| [14] | 陈峰, 张静, 韩二牛, 温苏雅拉图null, 李盛林, 王国林, 王磊, 王少昆. 乌拉特天然梭梭( Haloxylon ammodendron )林土壤微生物多样性及其与土壤性质的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 207-214. |
| [15] | 闫沛迎, 屈建军, 杨自辉, 肖建华, 唐进年. 不同生物气候区生物土壤结皮蓝藻物种多样性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 85-94. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
